What Are Signs of Behavioral Problems? Have you ever noticed actions or habits in someone—maybe even in yourself or your child—that just don’t feel quite right?
Little things like constant outbursts, avoiding others, or sudden mood swings might seem small at first. But they could be pointing to something deeper. Understanding signs of behavioral problems can feel overwhelming, especially when you’re unsure what to look for. Are these normal behaviors or something that needs attention?
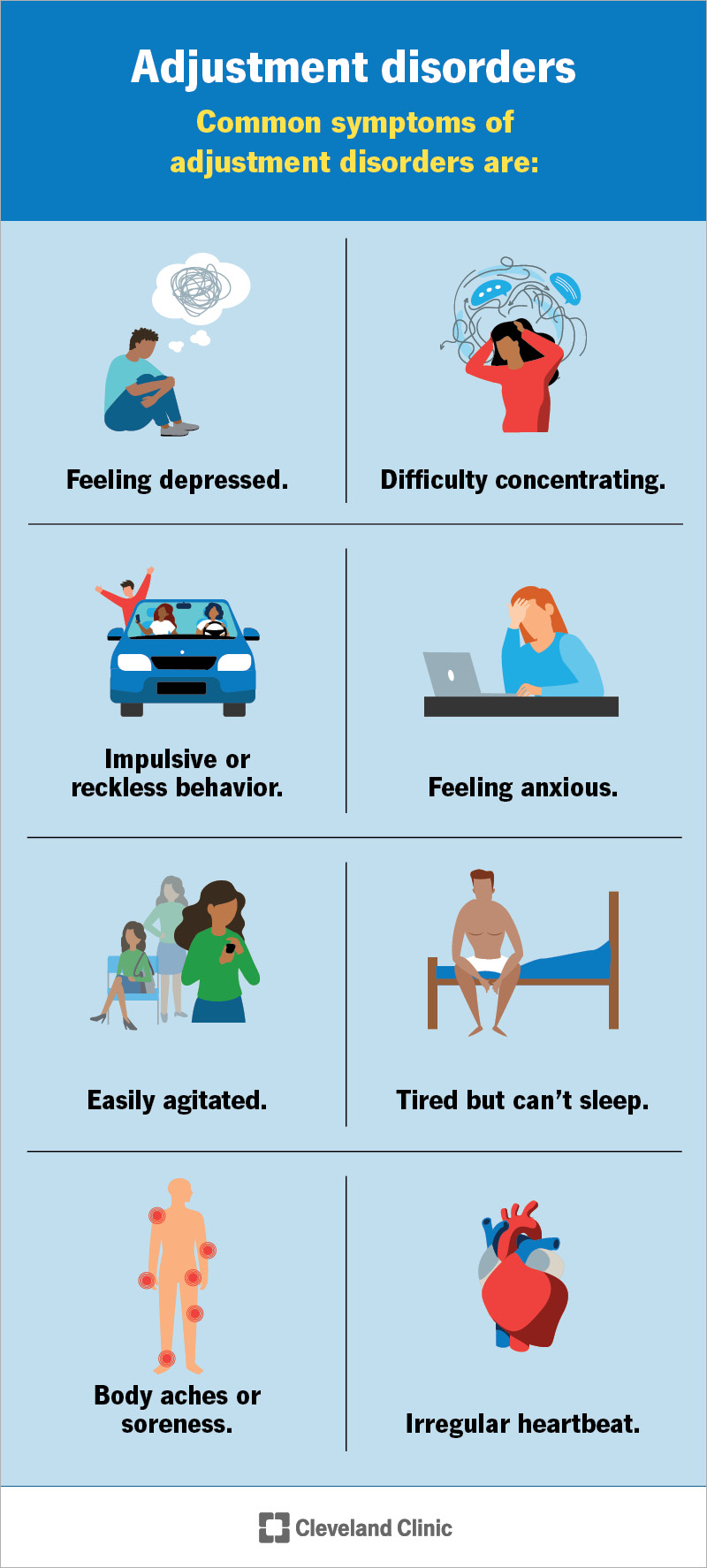
The uncertainty can leave you feeling frustrated, worried, or even helpless. Here’s the good news: spotting the signs of behavioral problems isn’t as complicated as it might seem. And once you recognize these signs, you’re one step closer to finding clarity and solutions. You’ll discover the most common signs to watch for and gain insights into what they might mean. In pediatric care, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends routine screening for mental, emotional, and behavioral concerns during well visits (updated 2025-08-28). Staying informed could make all the difference for you and the people you care about.
Credit: my.clevelandclinic.org
Early Warning Signs
Behavioral problems in children can show subtle signs early on. Recognizing these signs can help address issues before they escalate. Early detection often leads to better outcomes for the child. Parents, teachers, and caregivers must stay alert to changes in behavior.
These signs might not always seem serious initially. Yet, consistent patterns can point to underlying concerns. Behaviors that are persistent, severe, or uncommon for a child’s age warrant evaluation by a healthcare professional. Below are key early warning signs to watch for in children.
1. Frequent Temper Tantrums
Children may throw tantrums occasionally, but frequent episodes are concerning. If tantrums occur daily or last for extended periods, it may indicate frustration or emotional struggles. Persistent tantrums often need professional attention to uncover the root cause.
2. Difficulty Following Rules
Struggling to follow rules or instructions can be an early sign. This includes ignoring directions or repeatedly breaking rules at home or school. Such behavior may stem from defiance, attention struggles, or developmental delays.
3. Aggressive Behavior
Hitting, biting, or yelling often signals behavioral concerns. Aggressive actions toward peers, adults, or animals require immediate attention. This behavior might reflect anger issues, stress, or difficulty managing emotions.
4. Social Withdrawal
Some children avoid social interactions or isolate themselves. They may prefer to stay alone rather than playing with peers. Social withdrawal could indicate anxiety, low self-esteem, or early signs of depression.
5. Excessive Fear Or Worry
Children showing constant fear or worry may be struggling internally. They might express concerns about situations that seem minor. Excessive anxiety can interfere with their daily activities and relationships.
6. Trouble Paying Attention
Difficulty staying focused during tasks or activities is another red flag. Children may get easily distracted or fail to complete assignments. This often points to attention deficits or other learning challenges.
7. Disruptive Sleep Patterns
Changes in sleep, like trouble falling asleep or staying asleep, are important. Poor sleep can impact mood, energy, and behavior. It might also be linked to stress or underlying emotional struggles.

Credit: www.felixhospital.com
Common Behavioral Issues
Behavioral problems can disrupt daily routines and relationships. Identifying these issues early helps manage their impact. Understanding common behavioral challenges is key to addressing them effectively.
Some behaviors might seem minor but can signal deeper concerns. By recognizing these signs, you can take steps toward a solution.
Disruptive Behaviors
Disruptive behaviors interrupt normal activities or conversations. Examples include yelling during quiet times or refusing to follow instructions. These actions often affect group settings, making cooperation difficult.
Aggressive Actions
Aggression can involve hitting, biting, or throwing objects. These actions may stem from frustration or difficulty expressing feelings. Aggressive behaviors can harm relationships and personal safety.
Defiance Or Resistance
Defiance is shown through refusal to comply with rules or requests. This behavior can appear as ignoring instructions or arguing with authority figures. Persistent defiance may signal deeper emotional struggles.
Social Withdrawal
Social withdrawal includes avoiding interactions or isolating from others. This might involve skipping social events or staying silent in group settings. It often reflects feelings of anxiety or low self-esteem.
Impulsivity
Impulsivity leads to acting without thinking of consequences. Examples include interrupting conversations or making risky decisions. This behavior can create challenges in school, work, or relationships.
Difficulty Managing Emotions
Struggling to manage emotions can result in frequent outbursts or mood swings. This often involves crying, shouting, or shutting down during stressful situations. Emotional challenges can interfere with problem-solving and communication.
Emotional Triggers
Behavioral problems often stem from emotional triggers that can be difficult to identify but crucial to address. Emotional triggers are those internal or external events that spark an intense emotional reaction, often leading to disruptive behaviors. Recognizing these triggers can help you better understand what’s behind certain actions and guide you toward meaningful solutions.
What Are Emotional Triggers?
Emotional triggers are situations, words, or environments that provoke a strong emotional response. These responses are often disproportionate to the situation at hand. For example, a child might have a full-blown meltdown over a small change in their routine, or an adult might lash out after a seemingly harmless comment.
These reactions often mask deeper feelings like fear, frustration, or insecurity. By identifying the triggers, you can move closer to resolving the root cause rather than just addressing the surface behavior.
Common Emotional Triggers To Watch For
Everyone has unique triggers, but some are more common when it comes to behavioral problems. Here are a few:
- Criticism:Feeling judged or criticized, even constructively, can provoke defensive or aggressive reactions.
- Unmet Expectations:When things don’t go as planned, it can lead to anger, disappointment, or anxiety.
- Past Trauma:Certain words, places, or situations can remind someone of a painful experience, causing them to react emotionally.
- Lack of Control:Feeling powerless or out of control can spark frustration or defiance.
Take a moment to think about your own triggers. What situations consistently push your buttons? This reflection can help you empathize with others experiencing similar struggles.
How To Spot Emotional Triggers In Others
Watching for patterns in behavior is key. Does someone consistently act out in specific situations, like group settings or after a long day? This might point to an emotional trigger.
Pay attention to physical cues as well. Clenched fists, a tense jaw, or a sudden change in tone can signal emotional distress. These signs are often the body’s way of expressing what words cannot.
Ask yourself: Are you observing a reaction to a single event, or does this happen repeatedly? Patterns often reveal the underlying issues.
Practical Tips To Address Emotional Triggers
Once you identify emotional triggers, take small, actionable steps to manage them. Here are some ideas:
- Pause and Reflect:Encourage the person to take a moment to breathe before reacting. This can help diffuse the immediate emotional response.
- Communicate:Talk about the trigger in a calm, non-judgmental way. Ask open-ended questions like, “What made you feel this way?”
- Adjust the Environment:If possible, remove or modify the trigger. For example, if a crowded room causes anxiety, find a quieter space.
- Focus on Solutions:Work together to create strategies for handling similar situations in the future.
Remember, addressing emotional triggers takes time and patience. Small changes can lead to big improvements over time.
Why Emotional Triggers Matter
Ignoring emotional triggers can worsen behavioral problems, making them harder to tackle later. Addressing them, on the other hand, can improve relationships and overall well-being. It also builds emotional resilience, helping the individual better cope with future challenges.
What triggers have you noticed in yourself or those around you? Taking the time to reflect on this could be the first step toward positive change.
Impact On Social Skills
Difficulty interacting with peers may signal behavioral problems. Struggles with sharing or maintaining conversations often affect social skills development. These challenges can hinder forming connections.
Impact on Social Skills Behavioral problems don’t just affect how kids feel or act—they can also disrupt how they connect with others. Social skills are often the first to take a hit, leaving children feeling isolated or misunderstood. If you’ve noticed your child struggling to maintain friendships, it might be time to dig deeper. Children with behavioral issues may find it hard to read social cues, share, or take turns. This can lead to awkward interactions and even conflicts. Let’s break this down further: —
Struggles With Teamwork
Group activities, whether in class or during playdates, can become overwhelming. A child with behavioral problems might dominate conversations or refuse to compromise. This can push peers away and make collaborative tasks frustrating for everyone involved. Imagine a child refusing to share their blocks during playtime. Their peers may feel excluded and stop inviting them to join in. Have you noticed similar patterns in your child? —
Difficulty Maintaining Friendships
Friendships require empathy, trust, and patience—skills that don’t always come easily to children with behavioral challenges. They may unintentionally hurt others’ feelings by saying something inappropriate or acting impulsively. For example, a child who interrupts constantly might be seen as rude, even if they don’t mean harm. Over time, this can create a cycle where they lose friends and feel rejected. —
Trouble Understanding Boundaries
Kids with behavioral problems might not recognize personal boundaries, either physical or emotional. This can make others uncomfortable. They might invade personal space, interrupt conversations, or ask intrusive questions. A child who hugs classmates without asking may think they’re being friendly. But to their peers, it could feel too much, too soon. Learning to respect boundaries is crucial for healthy relationships. —
Increased Risk Of Bullying
Children with noticeable behavioral challenges often become easy targets for bullies. Their differences can make them stand out, and their reactions might fuel further teasing. Think about a child who cries or lashes out when teased. Instead of stopping, bullies may see this as a reason to continue. Helping your child develop coping strategies is key to breaking this cycle. —
Withdrawal From Social Interactions
Sometimes, children with behavioral problems avoid social situations altogether. They may feel safer alone than risk being judged or rejected. Over time, this can lead to loneliness and even anxiety. Picture a child sitting alone at lunch, avoiding eye contact. While it might seem like they prefer solitude, it’s often a sign they feel out of place. How can you help them step out of their shell? — The good news? Social skills can be taught and improved. Small steps like role-playing scenarios, practicing active listening, or joining structured activities can make a huge difference. Keep the focus on progress, not perfection. What small change can you make today to support your child’s social growth?
When To Seek Help
Recognizing when behavioral problems require professional help can be challenging. You might wonder, “Is this just a phase, or is something deeper going on?” The truth is, knowing when to seek help could make a big difference for your child or loved one. Let’s break down the signs that suggest it’s time to reach out to a professional.
Changes That Last Too Long
It’s normal for kids or adults to go through rough patches. A bad mood, stress from school, or work pressure can lead to temporary shifts in behavior. But if these changes last for weeks or months, it’s time to pay closer attention.
For instance, has your child been consistently withdrawn, refusing to talk or engage in activities they once loved? Or maybe your partner seems stuck in anger or sadness that doesn’t ease over time. Long-lasting changes signal that something deeper might be happening.
Behavior That Disrupts Daily Life
Ask yourself: is this behavior interfering with their ability to live their life? If tantrums, aggressive outbursts, or extreme anxiety are stopping your loved one from going to school, doing their job, or interacting socially, it’s a serious red flag.
These disruptions don’t just affect the person showing the behavior—they impact everyone around them. You may find yourself constantly adjusting your routine, avoiding certain situations, or feeling exhausted trying to manage the fallout.
Physical Complaints With No Clear Cause
Behavioral problems don’t always show up emotionally or socially. Sometimes, they manifest physically. Frequent headaches, stomachaches, or unexplained fatigue could be linked to anxiety, depression, or stress.
I once had a friend whose child constantly complained of stomach pain. After medical tests ruled out physical issues, therapy revealed the child was overwhelmed by bullying at school. If physical symptoms persist, don’t overlook the emotional connection.
Signs Of Harmful Behavior
If someone is showing signs of self-harm or talking about wanting to hurt themselves, take it seriously. Don’t assume they’re “just seeking attention” or will “snap out of it.” Threats or actions of harm require immediate intervention.
U.S. safety note: If you or someone you know is in crisis, call or text 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline or chat via 988lifeline.org. In an emergency or if there is immediate danger, call 911. If you’re outside the U.S., contact local emergency services.
Trust Your Instincts
You know your child or loved one better than anyone else. If their behavior feels “off,” trust your gut. You don’t need a professional to validate that something isn’t right before you act.
It’s better to seek help early than to wait and regret it later. Even if it turns out to be a passing phase, having a professional assess the situation can provide peace of mind—or an early solution. Pediatric organizations recommend routine screening and early evaluation when concerns persist or affect functioning.
So, what’s holding you back from reaching out for help? Sometimes, the hardest part is taking that first step. But when you do, you’re opening the door to support, understanding, and the possibility of change.
Building Positive Habits
Building positive habits is key to managing behavioral problems effectively. Often, small changes in daily routines can make a significant difference in shaping a child’s behavior. But how do you know which habits to build and how to start?
1. Encourage Consistency In Daily Routines
Children thrive on structure and predictability. Set fixed times for meals, bedtime, and homework. This not only reduces anxiety but also helps them understand what’s expected of them.
Let’s say your child struggles with tantrums during bedtime. A calming routine—like reading a favorite book or dimming the lights—can signal it’s time to unwind. Over time, this habit can replace chaotic evenings with peaceful ones.
2. Praise Positive Behavior Immediately
Catch your child doing something good, and let them know you noticed. A simple “I love how you shared your toys today!” can reinforce good habits.
Be specific in your praise. Instead of a generic “Good job,” say what they did right. This helps them repeat the behavior because they understand what you appreciated.
3. Set Realistic Goals Together
Work with your child to set achievable goals. If they struggle with focus, start with a small task like completing homework for 10 minutes without distractions.
Celebrate small wins. A sticker chart or a high-five can show them progress is worth the effort. Building habits is a marathon, not a sprint, so keep the goals manageable.
4. Model The Behavior You Want To See
Your actions speak louder than words. If you want your child to be patient, show patience when you’re frustrated.
Think about this: How often do you put your phone down when asking them to do the same? Children mirror what they see, so be the example they need.
5. Limit Negative Reinforcement
Try not to focus solely on punishment when bad behavior occurs. Instead, redirect their attention to what they can do better next time.
If your child shouts when upset, teach them to use words to express their feelings. Offer alternatives rather than just saying, “Don’t do that.”
6. Stay Patient And Flexible
Building habits takes time, and setbacks will happen. Focus on progress rather than perfection.
If something isn’t working, be open to trying a new approach. The key is consistency, not rigidity, in helping your child build positive habits.
What small habit can you start encouraging today? Sometimes, the tiniest changes lead to the biggest breakthroughs.

Credit: valleyspringrecovery.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Symptoms Of Behavioral Disorder?
Symptoms of behavioral disorders include aggression, impulsivity, defiance, difficulty following rules, frequent tantrums, poor social skills, and emotional instability.
Does My Child Have Behavioral Problems?
Signs of behavioral problems include aggression, defiance, frequent tantrums, or difficulty following rules. Consult a pediatrician or specialist for evaluation.
What Are The Symptoms Of Disruptive Behavior?
Symptoms of disruptive behavior include frequent anger, defiance, aggression, rule-breaking, tantrums, arguing, and difficulty following instructions. Social conflicts, lack of focus, and impulsivity may also occur.
What Is Considered A Behavioral Problem?
A behavioral problem refers to actions that disrupt normal functioning, such as aggression, defiance, impulsivity, or difficulty following rules.
Conclusion
Recognizing behavioral problems early can make a big difference. Pay attention to sudden changes in actions, mood, or communication. Small signs may point to larger challenges needing support. Always approach concerns with patience and understanding. Speak to a trusted professional if issues persist or worsen.
Addressing these problems early helps create a healthier environment for growth and learning. Every step toward understanding behavior builds stronger relationships. Stay mindful, supportive, and proactive in handling these situations. Small efforts can lead to positive changes over time. This article is for educational purposes and does not replace professional medical advice.